CURRENT RESEARCH
Rural Economy-wide Impacts of Kenya's Home-Grown School Meals Program
This study highlights that school feeding programs not only improve children’s human capital outcomes but also create economic benefits for rural economies.
The Cost of Inaction: Impacts of WFP Assistance Shortfalls on Food Security Outcomes in Somalia and Uganda
The Cost of Inaction study, conducted for WFP, analyzed the potential consequences of reductions of up to 50% in WFP assistance to beneficiary households in Somalia and to refugee households in Uganda, Africa’s largest refugee-host nation. By combining LEWIE simulations and econometric analysis, it shows how these cuts are likely to impact the food security outcomes of not only beneficiaries but also nonbeneficiaries who do not receive WFP assistance.
General Equilibrium Models for an Ex-ante Evaluation of Different Food Procurement Modalities under the School Feeding Program in Senegal
The Government of Senegal’s on-going school feeding program (SFP) provides support to schools in the form of food, cash, or vouchers. The primary goal of the program is to improve children’s nutrition and health, school attendance, and capacity to learn.
Consultancy to Develop a Local Economy-wide Impact Evaluation (LEWIE) Model for Malawi
Kagin’s Consulting LLC, together with the International Food Policy Research Institute, will develop a Local Economy-wide modeling framework covering a series of districts in Malawi and implement a series of quantitative modeling analyses of the multiplier impacts of two interventions: rural road improvement and matching grants to private-sector agriculture firms who engage smallholders in commercial value chains. This work will support the Millennium Challenge Corporation compact development process in this country.
ECONOMIC IMPACT ASSESSMENT OF WORLD FOOD PROGRAM EXPENDITURES IN EAST AFRICA
The World Food Programme (WFP) spends more than USD 745 million annually in Regional Bureau of Nairobi (RBN) countries. In 2019, the RBN region moved 1.1 million MT of food throughout East Africa. It disbursed USD 270 million in cash to 5.4 million beneficiaries in the countries covered by RBN. It procured and supplied more than 500,000 MT of food from local, regional, and global sources. These numbers increased with the inclusion of Sudan in the RBN beginning in December 2020. This spending is vital to the humanitarian operations of the WFP. It also affects RBN economies, potentially creating large income and production impacts in the region. This study documents the “economic footprint” of WFP operations in East Africa.
Assessing the Economic Impacts of Protected Areas on Regional Economies in Zambia, Fiji, Nepal, and Brazil
Protected areas serve as a critical refuge for endangered biological resources. They also can create economic benefits as nature tourist destinations. Benefits include park entry fees and the income tourists spend at lodges and other tourism businesses, but they also include the many indirect effects that visitor spending creates for businesses and households around the parks and in nearby market towns.
Integrated Demand Analysis Platform: Economic Disruptions Caused by COVID-19
This project supported the World Food Programme (WFP) and Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) in better understanding economic disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic on households and at the local economy level. It aimed to facilitate emergency response and country-specific situation analysis as a consequence of the COVID-19 outbreak. Swift response models are vital tools for emergency assistance agencies. The COVID-19 pandemic revealed the lack of economic models for short-run policy relevant research to anticipate local impacts and design effective policy responses. This project developed and implemented a new micro general-equilibrium (GE) modeling approach to quickly simulate impacts of the pandemic and lockdowns on poor and non-poor rural and urban households across sub-Saharan Africa.
Beyond Experiments: Local Economy-wide Impact Evaluation
Includes studies carried out with the IADB, World Bank, FAO, UNICEF, and other organizations
This book and accompanying website show how to use general-equilibrium simulation methods to document direct and spillover effects of government policies, development projects, and other treatments. This book won the AAEA Quality of Communications Award.
Agricultural Development Impact Evaluation
This article in the recent Handbook of Agricultural Economics reviews studies of impacts of agricultural interventions as well as of other treatments on agricultural outcomes, showing that no single tool is sufficient to evaluate impacts; different methods are appropriate in different situations; all methods have weakness as well as strengths; and combinations of approaches often can offer a deeper and more reliable understanding of impacts than stand-alone methods.
Local-economy impacts of poverty programs in seven African countries
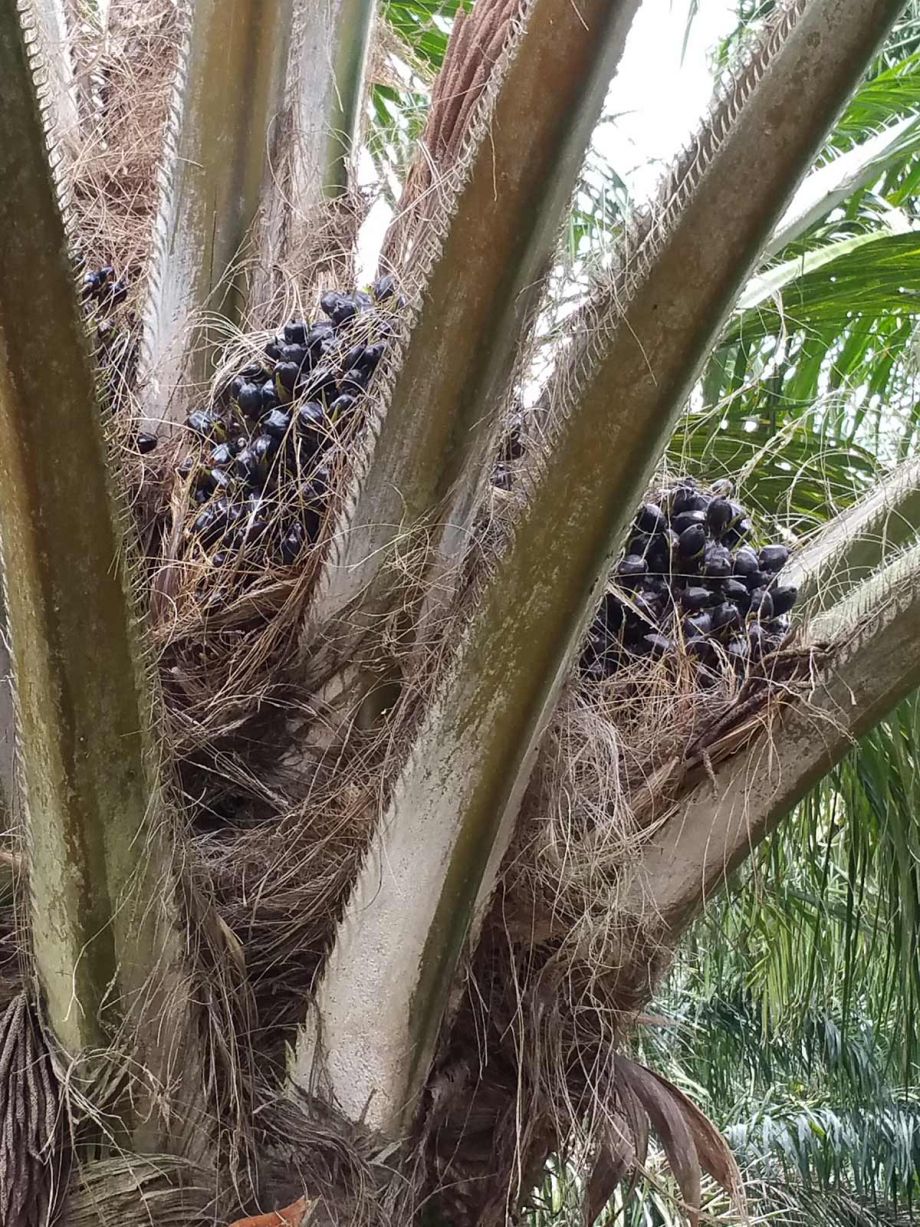
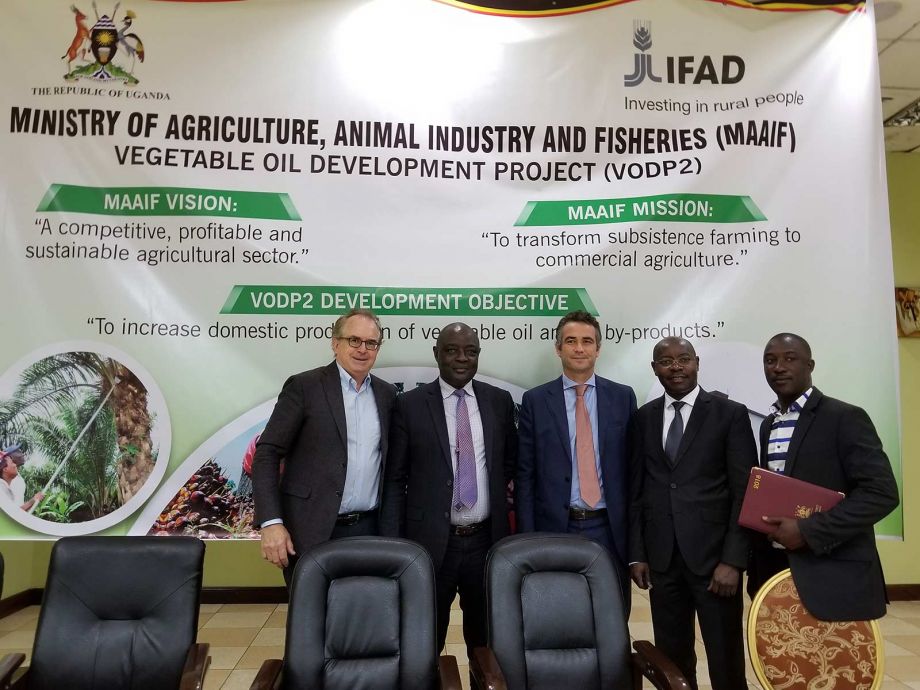
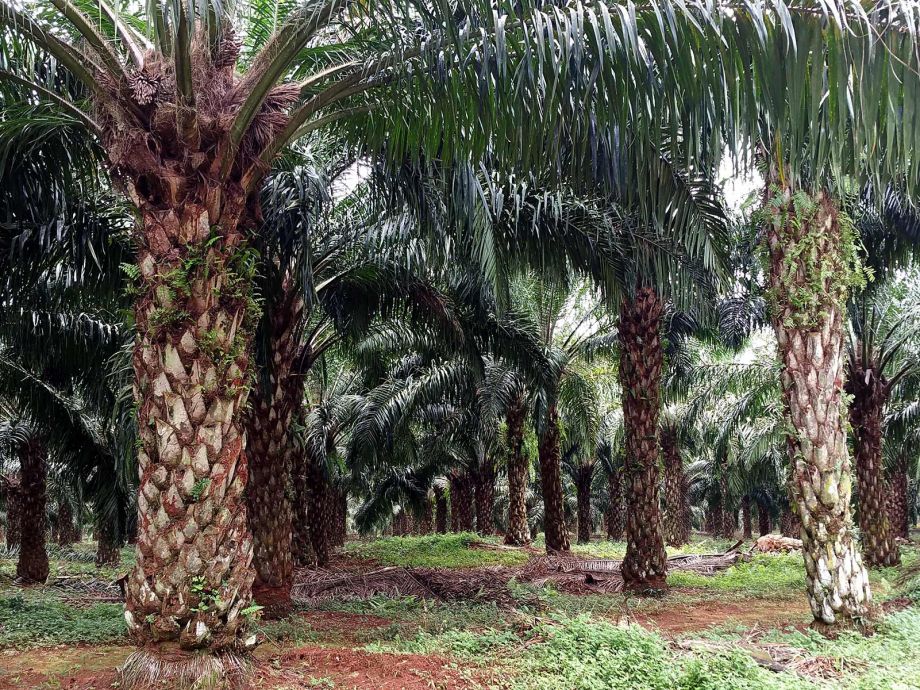
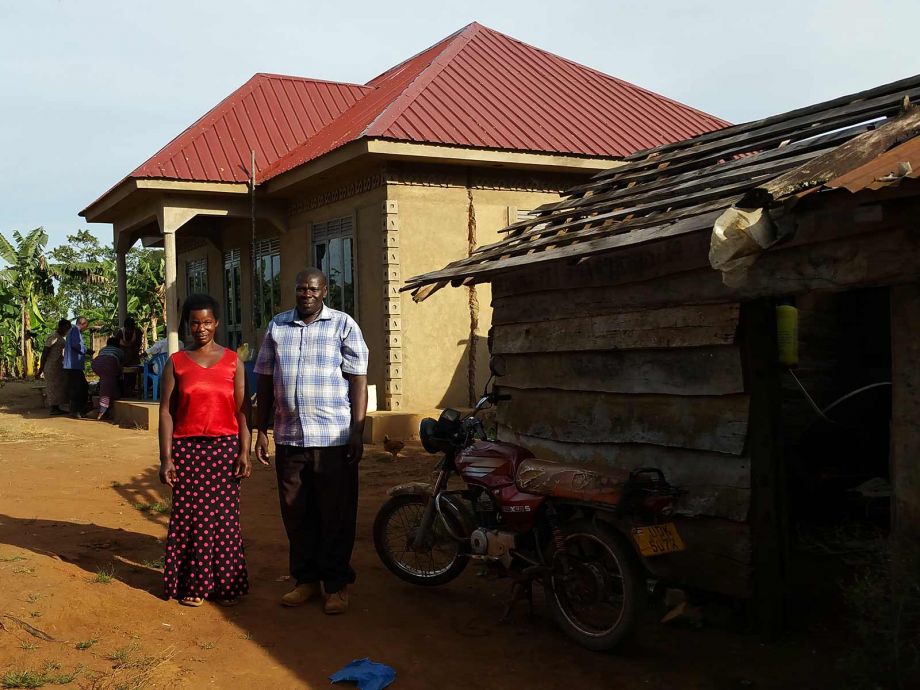
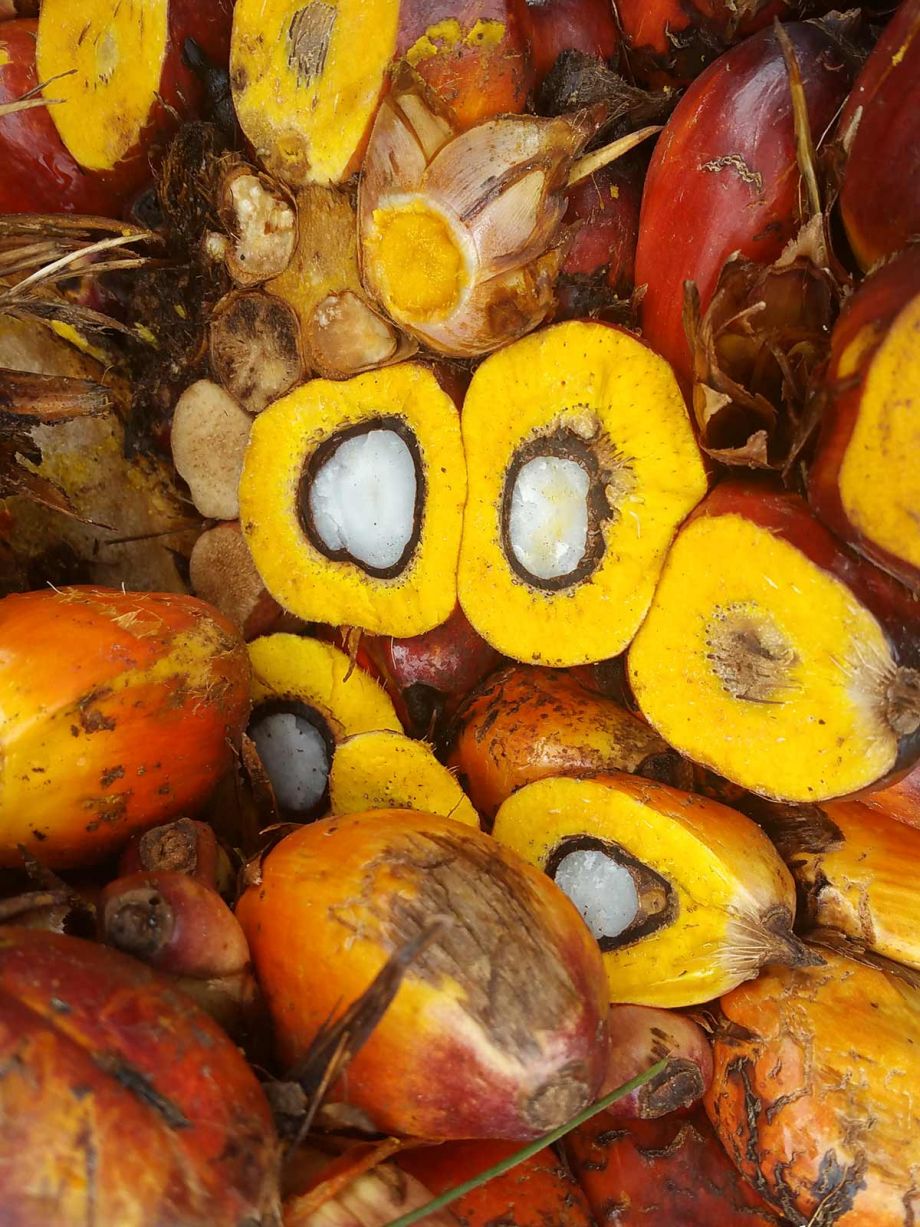
IMPACTS OF OIL PALM DEVELOPMENT IN UGANDA
A local economy-wide impact evaluation (LEWIE) simulation model is used to quantify the full impact of a large-scale oil palm production and processing project on residents of Bugala Island in Uganda’s Kalangala District. We use an econometric analysis of data collected from grower and non-grower households to validate findings on selected outcomes.
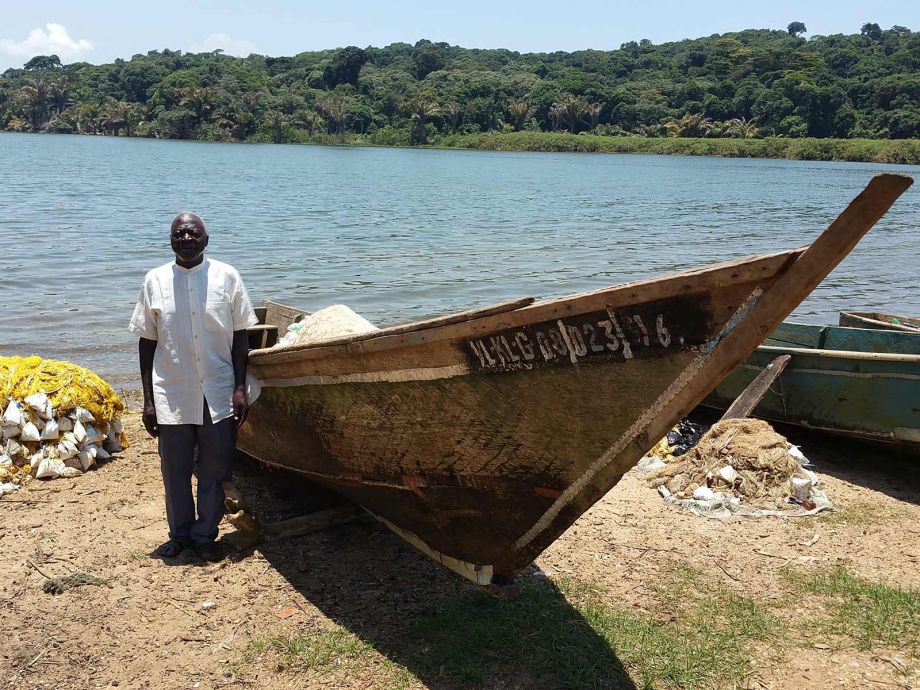
IMPACTS OF FISHERY REGULATION ON LOCAL ECONOMIC WELFARE
A series of projects by IDRA affiliates expands the focus of fishery research from individual fishers to whole fishing communities. Interactions among fishing and non-fishing households and activities shape the impacts of fishery reforms on welfare and poverty, as well as the sustainability of the fisheries, themselves. One of our most recent studies won the Best Article of 2023 award from the journal Marine Resource Economics.
ECONOMIC IMPACTS OF TOURISM
This paper was written to make development practitioners aware of simulation approaches for tourism impact analysis and of how to integrate these approaches into their project proposals, budgets, and terms of reference for expert consultants. Simulation approaches are particularly useful when experimental or economic approaches for project evaluation are not feasible.